Niacinamide in Skin Care
Niacinamide, also called nicotinamide or Vitamin B3, is unique because it has many benefits that other skin care ingredients do not have. It has so many skin benefits that it is one of the best ingredients to look for in skincare products for sensitive skin, hyperpigmentation and skin aging.
I am a dermatologist who does research on skincare ingredients and skin types and niacinamide is one of the best skincare ingredients because it play an important role in so many cellular functions. It is similar to NAD. This blog will explain why niacinamide is one of the best cosmeceutical ingredients. It is used to slow aging, soothe skin and decrease skin pigment.
What is Niacinamide?
Niacinamide is a water-soluble form of vitamin B3 that is involved in many metabolic pathways, such as the synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, and steroids, and in energy production in the NAD pathway. Niacinamide acts as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and its phosphorylated form (NADP+), which are essential coenzymes in cellular redox reactions and play a crucial role in mitochondrial function and ATP synthesis. It is a very important molecule that the body needs to be healthy.
Niacinamide Benefits
My patients often ask me what Vit B3 is good for and how it can benefit their skin. Sometimes it just sounds too good to be true that they are skeptical. But there is a lot of evidence based data to support the use of niacinamide. I will talk about these studies later in this blog. But first- lets look at all the things niacinamide can do for your skin.
Put simply, Vit B3 improves many skin issues such as:
- Dark spots
- Inflammation
- Skin Aging
It is one of my top recommendations for relieving inflammation and irritation in sensitive skin. It calms redness from conditions like rosacea, and other types of sensitive skin. It acts as a PAR-2 inhibitor which gives it these unique anti-inflammatory abilities and helps prevent hyperpigmentation by blocking the transfer of melanin.
Niacinamide has 3 main functions in a skin care routine:
- Blocks transfer of melanin into skin cells
- Gives cells energy to help repair damage and make important components like collagen
- Decreases inflammation
Niacinamide is used in serums, sunscreens, and creams to treat dark spots, melasma, skin aging and rosacea. It may also be found in acne treatments but niacinamide is not the best treatment for acne.
What Niacinamide Does for Skin
Here are the primary pathways through which niacinamide benefits skin:
- Pigmentation:
- Niacinamide inhibits the transfer of melanosomes from melanocytes to keratinocytes, reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation and promoting a more even skin tone.
- It suppresses the activity of tyrosinase, a key enzyme involved in melanin synthesis, thereby decreasing melanin production.
- Niacinamide helps to prevent UV-induced pigmentation by reducing the damaging effects of UV radiation on the skin.
- Inflammation:
- Niacinamide exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
- It modulates the activity of inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, reducing their infiltration into the skin and preventing excessive inflammation.
- Niacinamide enhances the skin's barrier function, which helps to prevent the entry of irritants and allergens that can trigger inflammatory responses.
- Free Radicals:
- Niacinamide acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can cause oxidative stress and damage to skin cells.
- It helps to boost the skin's natural antioxidant defenses by increasing the production of glutathione, a potent antioxidant enzyme.
- Niacinamide protects against UV-induced oxidative stress by reducing the formation of ROS and enhancing the skin's repair mechanisms.
- Mitochondrial Activity:
- Niacinamide is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme essential for cellular energy production in the mitochondria.
- It helps to maintain optimal mitochondrial function by supporting the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis.
- Niacinamide has been shown to improve mitochondrial biogenesis, promoting the formation of new, healthy mitochondria in skin cells.
- By enhancing mitochondrial activity, niacinamide supports cellular energy production, which is crucial for various skin functions, including cell turnover, collagen synthesis, and wound healing.
As you can see, niacinamide plays a multifaceted role in skin health by modulating pigmentation, reducing inflammation, combating free radicals, and supporting mitochondrial activity. These diverse mechanisms contribute to its beneficial effects on skin appearance, texture, and overall health.
Antiaging
Vit B3 helps gives skin cells the energy they need to restore collagen. It also soothes inflammation that is known to cause skin aging. It is found in many antiwrinkle serums. Here are some of our favorite antiaging serums with Vit B3.
This antiaging cream has Vit B3 plus many ingredients to target cellular senescence, free radicals, inflammation and other causes of skin aging. This is a very hydrating antiwrinkle cream for dry aging skin types because of its superior barrier repair abilities. Perfect for sensitive skin.
This antiaging serum has NCEF which is essential hyaluronic acid, amino acids, and antioxidants in a liposome vehicle to help increase absorption. This serum has niacinamide and many hydrating and antiaging ingredients. It also has some comedogenic ingredients so do not use if you are an acne-prone skin type. This is best for women with dry skin types because it has a feminine fragrance.
This serum contains snail mucin, the antioxidant superoxide dismutase, and Vitamin C in addition to Vitamin B3. It even has soy proteins to help with estrogen deficient menopausal skin. Best for women with mature skin.
This Neocutis cream has growth factors and peptides and oils to hydrate skin. This is noncomedogenic but may be too heavy for very oily types and too light for very dry types. There is a richer version for very dry types. You can use this before or after a retinoid and after a VItamin C serum.
This Neocutis antiwrinkle cream is for very dry skin types because it has petrolatum in it which makes it feel greasier. It is a good choice for menopausal skin and because it has wild yam extract in addition to growth factors and peptides. It will help “slug in" any products that it is placed on top of, so use this over an antiaging serum at night to increase absorption.
Skin Lightening
Vit B3 is a PAR-2 blocker that helps lighten skin and prevent the recurrence of dark spots and an uneven skin tone. Niacinamide will help lighten skin but should be paired in the skin care routine with a retinoid and a tyrosinase inhibitor for best results.
Best products with niacinamide to lighten skin
These are our dermatologist recommended products with Vit B3 to use in a skin lightening routine.
-
Biopelle Brightening KNR Serum -This serum combines skin lighteners form 3 skin lightening ingredient categories: Vit B3, retinol and kojic acid
-
SkinCeuticals Discoloration Defense- This serum has 3% tranexamic acid, 1% kojic acid and 5% Vit B3
-
Medature Hydrobright- Combines hexylresorcinol, hyaluronic acid and Vit B3.
- Zerafite Brightening Barrier Cream- Combines unsaturated fatty acids, Vit B3, Camellia Japonica Seed Oil, Artemisia Capillaris Extract, Bilberry extract, and Ulmus Davidiana Root Extract
Eye Creams with Vit B3 to Lighten Dark Circles
Redness and Inflammation
Vit B3 is a good anti-inflammatory ingredient to treat rosacea or a red face.
In fact, it is one of the best ingredients for a redness on the face- unless you are allergic to it.
Top 3 niacinamide creams to treat facial redness
Sunscreen
Vit B3 gives cells energy to repair themselves after sun damage.
This is why niacinamide is a good ingredient in sunscreen.
Here are the best sunscreens that have niacinamide:
Acne
Niacinamide decreases inflammation which helps treat the symptoms of acne but not the cause. It should be combined with other ingredients to effectively treat acne such as benzoyl peroxide and retinoids.
Which acne ingredients are best to combine with niacinamide to treat acne depends upon your Baumann Skin Type.
Acne scars
Niacinamide does not help true acne scars.
However, when my patients say they have acne scars, they often are referring to the red marks left after a pimple heals. These pink or red marks are not scars- they are skin inflammation. It can speed up how fast the red spots from acne heal and disappear. It can be used on acne scabs to help them heal without a scar.
How long does Niacinamide Take to Work?
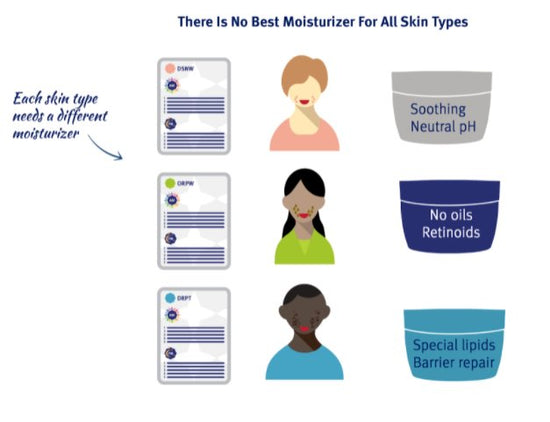
Niacinamide can help soothe upset skin within a few days but it can take 12- 16 weeks to see an improvement in dark spots. Niacinamide works faster when combined in the correct step order with other products in the skincare routine that help it work better . Which products to combine it with to speed results depends upon many things such as your Baumann Skin Type.
How Often To Use
Niacinamide is not irritating to the skin unless you have an allergy to it. It can be used once or twice a day in your skin care routine.
Is Niacinamide Better?
Trying to decide if Vit B3 is the best ingredient for you- or maybe vitamin c, retinoids, or HA serums are better.
Take the quiz and we will tell you exactly what skin care products to use for your skin type. Below I compare niacinamide to other skincare ingredients.
Niacinamide vs Vitamin C?
Vitamin C and Vit B3 are very different, and which to choose depends upon your Baumann Skin Type.
They both can be used to lighten dark spots, but Vitamin C is a tyrosinase inhibitor while niacinamide is a PAR-2 blocker.
- Niacinamide can be used on sensitive skin but Vitamin C should not be.
- Niacinamide sooths inflammation while Vitamin C can cause inflammation.
- Niacinamide can be used on a rash or burn, Vitamin C cannot.
Both are antioxidants and can be used for skin aging but they work differently:
- They both increase collagen production but through different mechanisms
- Niacinamide increases cellular energy, Vitamin C does not
- Niacinamide increases DNA repair, Vitamin C does not
- Vitamin C is an exfoliant and niacinamide is not.
Niacinamide vs Hyaluronic acid
These are very different types of skin care ingredients. Hyaluronic acid hydrates, plumps and makes other ingredients absorb better.
Niacinamide is anti-inflammatory, antiaging, increases cellular energy, and lightens skin.
Retinol vs Niacinamide
Both ingredients are good for antiaging, but retinol is better.
These can be used together because they both have antiaging and skin lightening benefits.
Vit B3 can help decrease the side effects from retinol.
If you have to choose between the two- choose retinol for antiaging.
Sun and Niacinamide
You can go in the sun while wearing niacinamide. Niacinamide does not seem to be a photoallergen and does not make skin more sensitive to sun.
Side Effects and Negative Effects
When used topically, it has very few negative effects. It gets blamed for rosacea flares and facial flushing but reactions are more likely due to an allergy.
Allergic reactions
Vit B3 can cause an allergic reaction in some people. The purity and grade of Vit B3 used in the skin care formulation effects the potential to cause a skin allergy. In other words- purer forms of are less likely to cause an allergic reaction.
This is why you may get an allergy to some products with niacinamide in them and not from others. In fact, it can vary from batch to batch depending on what form was used when the products were made.
Facial Flushing
When niacinamide is applied to the skin, it is readily absorbed and utilized by skin cells without triggering the release of prostaglandins, causing vasodilation. Niacinamide does not cause flushing.
Oral niacin, which is similar to niacinamide and is also known as nicotinic acid, can cause flushing, which is characterized by redness, warmth, and tingling sensations in the skin, particularly on the face, neck, and chest. This flushing occurs because niacin activates the GPR109A receptor in the skin, leading to the release of prostaglandins, which dilate blood vessels and increase blood flow to the skin.
In contrast, topical niacinamide, despite being in the same vitamin B3 family as niacin, does not cause flushing when applied to the skin. The reason for this difference is that niacinamide does not activate the GPR109A receptor like niacin does. Niacinamide is a more stable form of vitamin B3 that does not undergo the same metabolic processes as niacin when applied topically.
What can you not mix with niacinamide?
Although many people say you cannot mix niacinamide with Vitamin C, this is incorrect. Niacinamide and Vitamin C can be used together. Both are water soluble ingredients that are compatible together.

Skin care Ingredients Compatible with Niacinamide
You can mix Vit B3 with almost any skincare ingredients. It is a myth that you cannot use it a the same time as Vitamin C.
Niacinamide can be used with:
- AHAs like glycolic acid
- Antioxidants
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)
- BHA (salicylic acid)
- Hyaluronic acid
- Peptides
- Retinol and retinoids
Make sure you are using the best niacinamide products for your skin type.

What does niacinamide do?
It blocks the transfer of the pigment melanin into skin cells, it neutralizes free radicals, calms inflammation, and gives cells energy. These results in these benefits: soothing, skin lightening and antiaging.
What is niacinamide?
Niacinamide is like a helpful tool in our cells that helps create and use energy. It's part of a process that keeps our body running smoothly, and it can also calm inflammation and lighten skin.
Does niacinamide lighten skin permanently?
No, the effects of niacinamide are temporary. It acts as a temporary PAR-2 blocker. It must be used consistently every day to have lightening effects.
Can niacinamide cause acne?
It is not comedogenic does not cause acne but some impure forms can cause an allergic reaction.
Is niacinamide an active ingredient?
Yes it is considered active because it has many biologic effects.
Is niacinamide drying?
This ingredient does not dry out your skin or injure your skin barrier, however it can be mixed with other ingredients that cause skin dryness.
When to use niacinamide?
It can be used in any type of product any time of day.
Is niacinamide safe?
Yes it is safe unless you have a skin allergy to it.
What does niacinamide do to the skin?
It lightens the skin color and decreases redness and helps preven twrinkles.
What ingredients go with niacinamide?
Yes, you can mix Vit B3 with any skin care ingredients.
It does not react with anything.
Years ago there was a myth that it cannot be used with Vitamin C but that is not true.
What moisturizer goes well with niacianmide?
Any moisturizer will work well with niacinamide. Look for a moisturizer that is right for your Baumann Skin Type that has niacinamide it or layer a moisturizer over a niacinamide serum.
Best References and Scientific Publications on Niacinamide for Skin
- L. Baumann. Ch 44 Niacinamide in Cosmeceutical and Cosmetic Ingredients (McGraw Hill 2015)
- Leyden JJ, Shergill B, Micali G, Downie J, Wallo W. Natural options for the management of hyperpigmentation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011 Oct;25(10):1140-5.
- Zhu W, Gao J. The use of botanical extracts as topical skin-lightening agents for the improvement of skin pigmentation disorders. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2008 Apr;13(1):20-4.
- Greatens A, Hakozaki T, Koshoffer A, Epstein H, Schwemberger S, Babcock G, Bissett D, Takiwaki H, Arase S, Wickett RR, Boissy RE. Effective inhibition of melanosome transfer to keratinocytes by lectins and niacinamide is reversible. Exp Dermatol. 2005 Jul;14(7):498-508.
- Mohammed D, Crowther JM, Matts PJ, Hadgraft J, Lane ME. Influence of niacinamide containing formulations on the molecular and biophysical properties of the stratum corneum. Int J Pharm. 2013 Jan 30:441(1-2):192-201.
- Comaish JS, Felix RH, McGrath H. Topically applied niacinamide in isoniazid-induced pellagra. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Jan;112(1):70-2.
- Benavente CA, Schnell SA, Jacobson EL. Effects of niacin restriction on sirtuin and PARP responses to photodamage in human skin. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42276.
- Surjana D, Damian DL. Nicotinamide in dermatology and photoprotection. Skinmed. 2011 Nov-Dec;9(6):360-5.
- Namazi MR. Nicotinamide in dermatology: a capsule summary. Int J Dermatol. 2007 Dec;46(12):1229-31.
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, Greatens A, Hillebrand GG, Bissett DL, Boissy RE. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002 Jul;147(1):20-31.
- Konda S, Geria AN, Halder RM. New horizons in treating disorders of hyperpigmentation in skin color. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012 Jun;31(2):133-9.
- Zhu W, Gao J. The use of botanical extracts as topical skin-lightening agents for the improvement of skin pigmentation disorders. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2008 Apr;13(1):20-4.
- Gillbro JM, Olsson MJ. The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents—existing and new approaches. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2011 Jun;33(3):210-21.
- Surjana D, Damian DL. Nicotinamide in dermatology and photoprotection. Skinmed. 2011 Nov-Dec;9(6):360-5.
- Greatens A, Hakozaki T, Koshoffer A, Epstein H, Schwemberger S, Babcock G, Bissett D, Takiwaki H, Arase S, Wickett RR, Boissy RE. Effective inhibition of melanosome transfer to keratinocytes by lectins and niacinamide is reversible. Exp Dermatol. 2005 Jul;14(7):498-508.
- Sharlow ER, Paine CS, Babiarz L, Eisinger M, Shapiro S, Seiberg M. The protease-activated receptor-2 upregulates keratinocyte phagocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2000 Sep;113(Pt 17):3093-101.
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, Greatens A, Hillebrand GG, Bissett DL, Boissy RE. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002 Jul;147(1):20-31.
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, Greatens A, Hillebrand GG, Bissett DL, Boissy RE. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002 Jul;147(1):20-31.
- Elliott RB, Pilcher CC, Fergusson DM, Stewart AW. A population based strategy to prevent insulin-dependent diabetes using nicotinamide. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Sep-Oct;9(5):501-9.
- Gensler HL, Williams T, Huang AC, Jacobson EL. Oral niacin prevents photocarcinogenesis and photoimmunosuppression in mice. Nutr Cancer. 1999;34(1):36-41.
- Damian DL. Photoprotective effects of nicotinamide. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2010 Apr;9(4):578-85.
- Yiasemides E, Sivapirabu G, Halliday GM, Park J, Damian DL. Oral nicotinamide protects against ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression in humans. Carcinogenesis. 2009 Jan;30(1):101-5.
- Surjana D, Halliday GM, Martin AJ, Moloney FJ, Damian DL. Oral nicotinamide reduces actinic keratoses in phase II double-blinded randomized controlled trials. J Invest Dermatol. 2012 May;132(5):1497-500.[1]
- Callender VD, St Surin-Lord S, Davis EC, Maclin M. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011 Apr 1;12(2):87-99.
- Mohammed D, Crowther JM, Matts PJ, Hadgraft J, Lane ME. Influence of niacinamide containing formulations on the molecular and biophysical properties of the stratum corneum. Int J Pharm. 2013 Jan 30:441(1-2):192-201.
- Sivapirabu G, Yiasemides E, Halliday GM, Park J, Damian DL. Topical nicotinamide modulates cellular energy metabolism and provides broad-spectrum protection against ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression in humans. Br J Dermatol. 2009 Dec;161(6):1357-64.
- Otte N, Borelli C, Korting HC. Nicotinamide – biologic actions of an emerging cosmetic ingredient. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2005 Oct;27(5):255-61.
- Mohammed D, Crowther JM, Matts PJ, Hadgraft J, Lane ME. Influence of niacinamide containing formulations on the molecular and biophysical properties of the stratum corneum. Int J Pharm. 2013 Jan 30:441(1-2):192-201.
- Hakozaki T, Takiwaki H, Miyamoto K, Sato Y, Arase S. Ultrasound enhanced skin-lightening effect of vitamin C and niacinamide. Skin Res Technol. 2006 May;12(2):105-13.
- Bissett DL, Robinson LR, Raleigh PS, Miyamoto K, Hakozaki T, Li J, Kelm GR. Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation by topical N-undecyl-10-enoyl-L-phenylalanine and its combination with niacinamide. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009 Dec;8(4):260-6.
- Jerajani HR, Mizoguchi H, Li J, Whittenbarger DJ, Marmor MJ. The effects of a daily facial lotion containing vitamins B3 and E and provitamin B5 on the facial skin of Indian women: a randomized, double-blind trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010 Jan-Feb;76(1):20-6.
- Kimball AB, Kaczvinsky JR, Li J, Robinson LR, Matts PJ, Berge CA, Miyamoto K, Bissett DL. Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation after use of moisturizers with a combination of topical niacinamide and N-acetyl glucosamine: results of a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2010 Feb 1;162(2):435-41.
- Fu JJ, Hillebrand GG, Raleigh P, Li J, Marmor MJ, Bertucci V, Grimes PE, Mandy SH, Perez MI, Weinkle SH, Kaczvinsky JR. A randomized, controlled comparative study of the wrinkle reduction benefits of a cosmetic niacinamide/peptide/retinyl propionate product regimen vs. a prescription 0.02% tretinoin product regimen. Br J Dermatol. 2010 Mar;162(3):647-54.
- Bissett DL, Miyamoto K, Sun P, Li J, Berge CA. Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in aging facial skin. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2004 Oct;26(5):231-8.
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, Greatens A, Hillebrand GG, Bissett DL, Boissy RE. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol. 2002 Jul;147(1):20-31.
- Bissett DL, Miyamoto K, Sun P, Li J, Berge CA. Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in aging facial skin. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2004 Oct;26(5):231-8.
- Bissett DL, Oblong JE, Berge CA. Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatol Surg. 2005 Jul;31(7 Pt 2):860-5; discussion 865.
- Greatens A, Hakozaki T, Koshoffer A, Epstein H, Schwemberger S, Babcock G, Bissett D, Takiwaki H, Arase S, Wickett RR, Boissy RE. Effective inhibition of melanosome transfer to keratinocytes by lectins and niacinamide is reversible. Exp Dermatol. 2005 Jul;14(7):498-508.